|
Next: References
Up: Spinning the Web
Previous: GZIP
- Anchor
- A marker for the beginning or the end of a hypertext link.
- Anonymous FTP
- A method of using FTP without having to have an
account on the server system. On systems offering an anonymous FTP
service, the user names `anonymous' and `ftp' are recognized to
allow access using the user's email address as a password.
- Arena
- An experimental Web browser program, being developed at
CERN.
- Attribute
- A parameter of an HTML element, that modifies
its effect.
- Authoring tool
- A program which partially automates the process
of writing HTML.
- Body
- In reference to an HTML document, the main text part of
the document: its content.
- Browser
- A program which sends requests for resources across
networks and displays those resources when they are received.
Another name for a Web client program.
- Button
- A screen-layout term, meaning a graphical representation
of a button on an area of screen, designed to be `clicked on' or
otherwise selected, as a method of user input.
- CERN
- The European Laboratory for Particle Physics in Geneva,
Switzerland, where the Web was first developed. Has lent its name
to one of the most popular Web server programs, which was developed
there.
- CGI
- Common Gateway Interface. The standard interface between
HTTP servers and external programs.
- CWIS
- Campus-Wide Information Systems. Computer-based
integrated information systems providing information about various
aspects of a college campus. CWIS have been around for some time
and were originally developed on mainframe computers, but are now
available on a variety of platforms. The term has broadened to
include information systems in schools and other campus-type
institutions.
- Client
- A program requesting information from a server program.
In Web-speak the program that a person uses to browse the Web (also
called browser).
- Client-server architecture
- A basic concept used in computer
networking, wherein servers retrieve information requested by
clients, and clients display that information to the user.
- Container
- An HTML element that contains text. The term is also
used in SGML, with the same meaning.
- Clickable image
- An image displayed on a screen, which when
pointed at with a mouse or other pointing device, initiates some
action on the computer.
- Daemon process
- Used to denote a background system process on
UNIX which runs independently of any user who is logged-in. This
term has come into common usage on the Internet, to refer to server
programs running on other operating systems too.
- DTD
- Document Type Definition; an SGML description of a document
markup language (such as HTML).
- Element
- A structural part of an HTML or SGML document
- Entity
- An HTML symbol that represents a special character. An
SGML entity has a much wider use as a sort of macro and inclusion
facility. This form of entity may appear in future versions of HTML.
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- A standard Internet protocol which
allows files to be transmitted from one computer to another across a
network.
- Fill-out forms
- Often abbreviated to Forms. The main mechanism
whereby Web sites elicit information from Web users. User-entered
data is returned to the Web site encoded within a browser request.
- Free Software Foundation
- An organization dedicated to creating
fine, freely distributable software. Much widely used software,
such as the GNU utilities, orignates from the FSF. Their software
is not public domain, but rather is covered by a copyright statement
and license, the effect of which is to ensure that the software
remains freely available.
- GIF
- Graphics Interchange Format. A standard graphics file
format developed by CompuServe, Inc.
- Gopher
- A menu-based network information system devised at the
University of Minnesota.
- GNU
- Recursive acronym, which stands for `GNU is not UNIX'.
Used in relation to software from the Free Software Foundation,
including GNU Emacs, the GNU C compiler, gzip and much more.
- Head
- That part of a Web document, at the beginning, which
contains meta-information about the document.
- Host
- A computer attached to the Internet.
- Home page
- A Web page that is used as an individual user's
starting point, i.e. the page that is fetched when the user starts
his or her browser. It is also used to refer to the top level page
of a server, although this is more correctly termed a Welcome
Page.
- Hypertext
- Words or phrases in a document which when selected,
usually by clicking with a mouse, are used as links which summon up
other information.
- HTML
- HyperText Markup Language. The markup language used for
World Wide Web documents.
- HTTP
- HyperText Transfer Protocol. The Internet protocol that is
used to allow Web clients to retrieve information from Web servers.
- IAB
- Internet Architecture Board. The organization that creates
Internet standards.
- IANA
- Internet Assigned Numbers Authority. The central
registration authority for values used in Internet protocols. Part
of the IAB.
- IETF
- Internet Engineering Task Force. An organization composed
of working groups, open to all interested indiciduals, which designs
and updates protocols for the Internet.
- Image button
- See button.
- Image Map
- A form of clickable image in which different
computer actions are initiated according to which area of the image
is selected.
- Intelligent agent
- An automated network information gathering
tool, which cruises the Internet, searching indexes and databases
for the names of documents on subjects specified by the user. Sometimes
referred to as a Knowbot.
- Internet
- The global computer network of networks. When spelled
with a lower case i, the term refers to an interconnected
group of networks.
- IP Address
- Internet Protocol Address. A standardized method of
identifying a particular computer connected to a network. The IP
address is expressed as four numbers, separated by periods, each
less than 256, and provides a unique identifier for every computer
connected to a network, in much the same way as postal addresses
operate.
- ISO
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO is an
industry-wide body which defines network protocols.
- JPEG
- Joint Photographic Experts Group; also refers to the
graphics file format developed by that body.
- Kiosk-mode browser
- A browser program configured to allow
user access only to a restricted range of Web documents.
- Knowbots
- See Intelligent Agents.
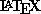 - A document preparation system devised by Leslie Lamport,
based on the
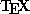 typesetting system. typesetting system.
- Line-mode browser
- A Web browser program which does not
have the facility to display images; one which displays text only.
- Markup language
- A language specially designed for the
processing, definition and presentation of text.
- Meta-information
- Information of a higher order: information
about information.
- MIME
- Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions. An extension to
the Internet mail standard, now often used to package multimedia
resouces being transmitted across networks.
- Mosaic
- The first widely-used graphical Web browser program,
developed at the NCSA.
- MPEG
- Motion Pictures Experts Group; also refers to the
format for files containing moving pictures developed by that group.
- NCSA
- The National Center for Supercomputing Applications, at
the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. The site where one
of the most popular Web browser programs, Mosaic, was developed.
- Network
- A generic term for physically separate computers
connected to each other by means of telecommunications hardware and
software.
- Network News
- Also known as USENET News - the Internet news
information service.
- NNTP
- Network News Transfer Protocol. Network News (sometimes
known as USENET News) is an Internet news information service. NNTP
is the transfer protocol used for moving news files around the
network.
- Node
- A physical sub-division of a logical Web document. When a
large Web document is divided into smaller sections to facilitate
rapid access across the net, each separate section is termed a node.
- Port
- A numeric identifier for an Internet service used to
distinguish between different services offered by hosts. Web
servers, for example, use port 80 by default. Network ports are
unrelated to hardware ports, such as printer ports on PCs.
- PostScript
- A page description language used by printers and
some window systems.
- PPP
- Point to Point Protocol. An Internet protocol for
connecting computers over a serial line.
- Protocol
- A standardized description of the messages that
computer programs exchange to communicate with each other over the
Internet so as to provide a particular service. Also used to refer
to the service, such as FTP, HTTP, and so on.
- RFC
- Request For Comments. The name given to discussion and
documentation papers for Internet standards.
- Resource
- An item of information provided on the Web. It was
felt that other terms such as document, were too narrow to
express the range of different media currently available, and likely
to become available in the future.
- Server
- A program that provides a service by responding to
requests from other client programs. The term is also used
to refer to the computer system on which the server program runs.
- Server side includes
- A Web server feature, which allows
information to be included into HTML documents by the server at the
time they are delivered to clients. This feature is implemented in
the NCSA server.
- Selector
- A string of characters used to specify a menu item to
a Gopher server. Analagous to a URL.
- SGML
- Standard Generalized Markup Language. A system for
describing markup languages, standardized as an international
standard, ISO 8879.
- SLIP
- Serial Line Internet Protocol. A protocol for connecting
computers using Internet protocols over a dial-up telephone line or
other serial line.
- SMTP
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol; the Internet electronic
mail transfer protocol.
- Tag
- An SGML character sequence that starts an element. The term
has the same meaning in HTML.
- TELNET
- A standard Internet protocol, providing a remote login
service.
- UDP
- User Datagram Protocol, one of the basic, low-level
standard Internet protocols.
- URC
- Uniform Reource Citation. A new Internet addressing
system, still under discussion, that will allow multiple copies of a
resource to be identified.
- URI
- Uniform Resource Identifier. A standard means of
addressing resources on the Web. See also URLs, URCs and URNs.
- URL
- Uniform Resource Locator. The current addressing scheme
for resources on the Web, which gives the location of a particular
copy of a resource.
- URN
- Uniform Resource Name. A new Internet addressing scheme,
still under discussion, which will allow multiple copies of a
resource to be identified.
- USENET News
- A popular networked discussion list system.
- Virtual document
- A document which does not exist as a physical
file, but which is generated in response to a request.
- WAIS
- Wide Area Information Service. A network information
system allowing searching of documents.
- Welcome Page
- The introductory Web page for a Web server, also
refered to as a home page.
- X Window System
- A networked windowing system developed by MIT
and now by the X Consortium that is commonly used on UNIX and VMS
systems.
- W3 Organization
- A recently-formed group, mostly composed of
organizations rather than individuals, who are working together to
coordinate the development of Web technology. Sometimes also known
as W3O.
- Wrapper program
- A short program or script, written to
encapsulate a larger program, often used to transform data into the
form required by the encapsulated program.
Next: References
Up: Spinning the Web
Previous: GZIP
![[ITCP]](itcp-mini.gif) Spinning the Web by Andrew Ford Spinning the Web by Andrew Ford
© 1995 International Thomson Publishing
© 2002 Andrew Ford and Ford & Mason Ltd
Note: this HTML document was generated in December 1994 directly from the
LaTeX source files using LaTeX2HTML. It was formatted into our standard page layout
using the Template Toolkit. The document is mainly of historical
interest as obviously many of the sites mentioned have long since
disappeared.
|